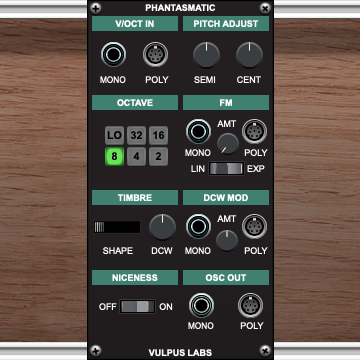
Prismatic - Phase Distortion Oscillator
Prismatic is a phase distortion oscillator inspired by the Casio CZ series synthesizers of the 1980s. It uses Digital Controlled Waveform (DCW) synthesis to morph smoothly between different waveforms, creating a wide range of timbres from smooth to aggressively digital.
Prismatic deliberately reproduces some of the limitations of 8-bit hardware (low-resolution wavetables, linear interpolation) to capture some of the sonic characteristics of 80s-era digital synthesis. Aliasing and quantisation noise are part of its sonic profile, and give its output a distinctly "retro" feel.
What is Phase Distortion?
Unlike traditional analog oscillators that generate fixed waveforms, phase distortion synthesis warps the phase of a sine wave before it's looked up in a wavetable. By changing how the phase accumulator maps to the sine table, you can transform a pure sine wave into sawtooth, square, or complex intermediate shapes.
The DCW (Digital Controlled Waveform) parameter controls this warping, letting you sweep continuously from one waveform to another - like morphing from a bright sawtooth through a sine wave to a hollow square wave.
Controls
V/OCT IN Section
MONO jack - Monophonic V/Oct pitch input POLY jack - Polyphonic V/Oct pitch input (16 voices)
Both mono and poly oscillators run simultaneously. The mono output is always active, while poly output is only processed when a cable is connected to the POLY output jack.
PITCH ADJUST Section
SEMI knob - Pitch adjustment in semitones (-7 to +7) CENT knob - Fine pitch adjustment in cents (-100 to +100)
OCTAVE Section
Six buttons for octave transposition:
- LO - 4 octaves down
- 32 - 2 octaves down
- 16 - 1 octave down
- 8 - No transposition (default)
- 4 - 1 octave up
- 2 - 2 octaves up
FM Section
MONO jack - Monophonic FM input POLY jack - Polyphonic FM input AMT knob - FM modulation amount (0 to 1) LIN/EXP switch - FM mode selector
Linear FM (LIN): Classic frequency modulation where the FM signal directly modulates the oscillator's frequency increment. This produces traditional FM synthesis sounds, with more dramatic effects at lower pitches.
Exponential FM (EXP): The FM signal modulates the V/Oct pitch exponentially. At full FM amount with ±5V input, you get ±1 octave of pitch variation. This creates through-zero FM effects and generates harmonic sidebands.
TIMBRE Section
WAVE switch - Four-position synthesis mode selector:
-
SAW ← [SINE] → SQUARE Default mode. Morphs from sawtooth through sine to square wave.
- Negative DCW: sawtooth-like timbres
- Center (DCW = 0): pure sine wave
- Positive DCW: square-like timbres
-
SQUARE ← [SAW] → SINE Morphs from square through sawtooth to sine wave.
- Negative DCW: square-like timbres
- Center: sawtooth-like timbre
- Positive DCW: sine wave
-
SINE ← [SQUARE] → SAW Morphs from sine through square to sawtooth.
- Negative DCW: sine wave
- Center: square-like timbre
- Positive DCW: sawtooth-like timbre
-
RESONANT Special mode with variable harmonic emphasis. The DCW control adjusts the frequency multiplier of a resonant oscillator that's amplitude-modulated by the main phase, creating sync-like timbres with controllable brightness.
- Negative DCW: lower frequency multiplier (1/2-1x)
- Center: 1x frequency multiplier
- Positive DCW: higher frequency multiplier (1-4x)
DCW knob - Digital Controlled Waveform parameter (-1 to +1) Sets the base timbre for the oscillator. The exact effect depends on the selected WAVE mode (see above).
DCW MOD Section
MONO jack - Monophonic DCW modulation input POLY jack - Polyphonic DCW modulation input AMT knob - DCW modulation amount (-1 to +1)
DCW modulation lets you animate the timbre in real-time, typically with envelopes or LFOs. The modulation amount is bidirectional - negative values invert the modulation.
QUALITY Section
NASTINESS knob - Audio quality control (4 positions)
This knob intentionally controls the "cleanliness" of the sound, with lower quality settings producing more aliasing and digital artifacts:
Position 0 - "Filtered" (Cleanest)
- 7kHz lowpass filter for anti-aliasing
- Linear interpolation used in upsampling from 16 to 48Khz
- Sub-sample phase precision (8-bit fractional phase)
- Best for clean, modern digital sounds
Position 1 - "Unfiltered"
- Linear interpolation used in upsampling from 16 to 48Khz
- Sub-sample phase precision
- No anti-aliasing filter
- Retains some high-frequency edge
Position 2 - "Interpolation Off"
- No sample interpolation in upsampling from 16 to 48Khz
- Sub-sample phase precision maintained
- More aliasing and digital artifacts
- Lo-fi retro character
Position 3 - "8-bit Realness" (Nastiest)
- No interpolation
- No sub-sample phase precision (phase truncated to 8 bits)
- Maximum aliasing and digital artifacts
- Pure retro 1980s digital aesthetic
Higher nastiness settings capture the gritty, aliased character of vintage digital synthesizers. Lower settings provide cleaner, more modern sounds.
OSC OUT Section
MONO jack - Monophonic oscillator output POLY jack - Polyphonic oscillator output (up to 16 voices)
Output range is approximately ±5V.
Technical Notes
- Sample rate: 48kHz (internally processed at 16kHz and upsampled)
- Phase resolution: 16-bit (65536 steps)
- Polyphony: 16 voices
- Wavetable resolution: 256 samples (8-bit)
- Fixed-point math throughout for authentic digital character
- CPU-efficient caching of frequency and DCW calculations
No reviews yet. Be the first to review this product!